Why Enterprises Are Hitting a Wall with N8n (And Moving to Agentic AI)
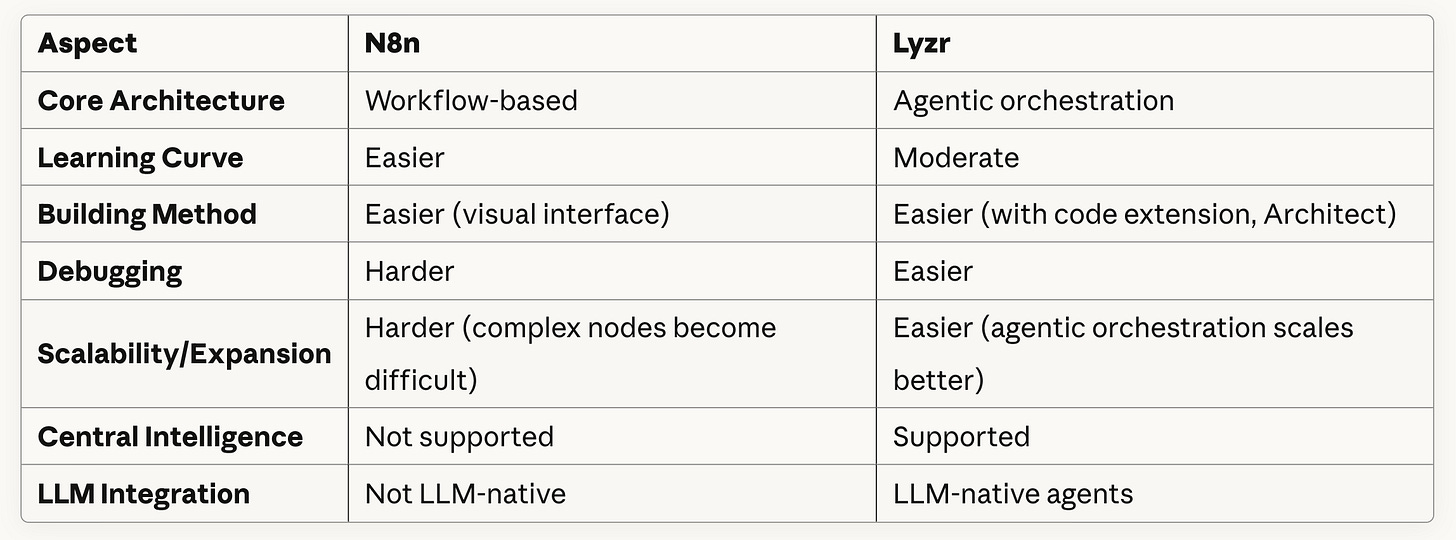
Lyzr is an Agentic AI platform. While N8n is a workflow platform.
I’m always asked, what is the difference? Why should we build on an agentic orchestration platform like Lyzr and not on N8n?
So here is my honest view.
And it is not just a view that I have formed by building on N8n, Lyzr, and other platforms like LangChain. It is also something that the enterprises are slowly realizing.
Just in the last three months, we’ve had at least five customers who have stopped their work on N8n for serious and complex workflows.
They have started building on Lyzr.
The Right Tool for the Right Job
For some simpler tasks, they continue to build on platforms like N8n or Make or Zapier, which I totally recommend them to do.
This works wherever they do not need a reasoning capability to come in.
But as soon as the requirement for reasoning ability comes into the picture, an agentic orchestration platform is better suited than N8n.
I’ll tell you why.
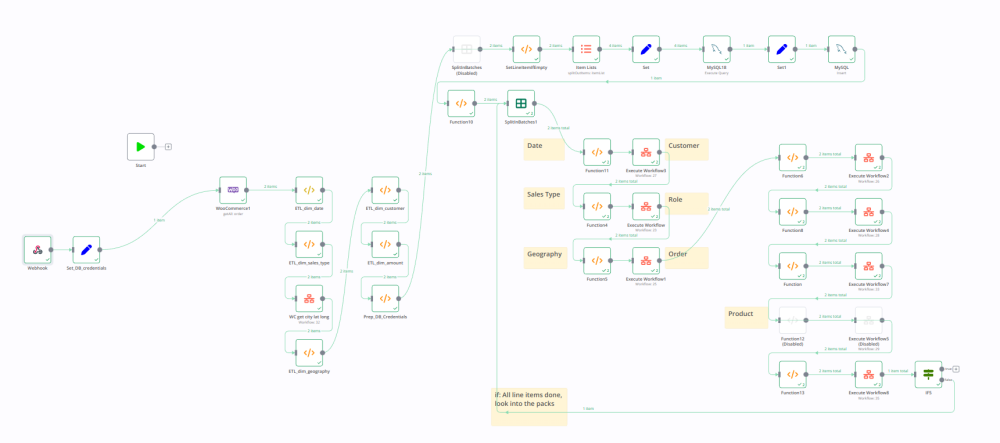
The “Spaghetti” Problem of Visual Workflows
When it comes to N8n, while it’s beautiful to see all those nodes and integrations, what we are essentially doing is establishing the logic in a more deterministic manner.
We’re defining how agents should work with one another, how they should retrieve data, or how they should call a tool.
This logic is expressed in the form of those connected lines, or also called “edges.”
If you see the N8n templates that you find in the market, even a medium complexity workflow ends up looking like spaghetti.
This is totally fine while building it.
But it is actually creating a lot of debt for enterprise organizations, and this will come back and bite you in the long run.
The Agentic Difference: Logic as Plain English
To understand this, you need to see how this looks very differently in the world of agentic orchestration.
See, in the world of agentic orchestration, the logic is not expressed as characters and edges that connect these nodes.
The logic is expressed as simple English text.
It’s just text. It’s just lines and lines of instructions.
The agent instructions hold the logic.
You can express them and read through them.
And you just connect one agent with another agent; you’re not necessarily taking them through a highly deterministic wired workflow.
This way, first of all, you are reducing the number of nodes compared to an N8n orchestration. This way, you are ensuring that your core logic is in plain English.
Where LLMs Thrive (And Where They Don’t)
And what are large language models? They are designed to be text models.
Having your entire logic written in natural language allows your large language models to come into play on the turf that they really understand.
They don’t have to unwind these complex N8n workflow templates to really figure out what is happening.
And this is the second big part: maintenance and debugging.
While N8n templates are easier to build, the maintenance and debugging are another large issue.
You need human help to debug and really figure out what is happening with the workflow.
Imagine someone built this workflow and moved on. Or you are adopting this N8n workflow from the market.
If you have to sit and debug, you have to again go through the whole logic yourself.
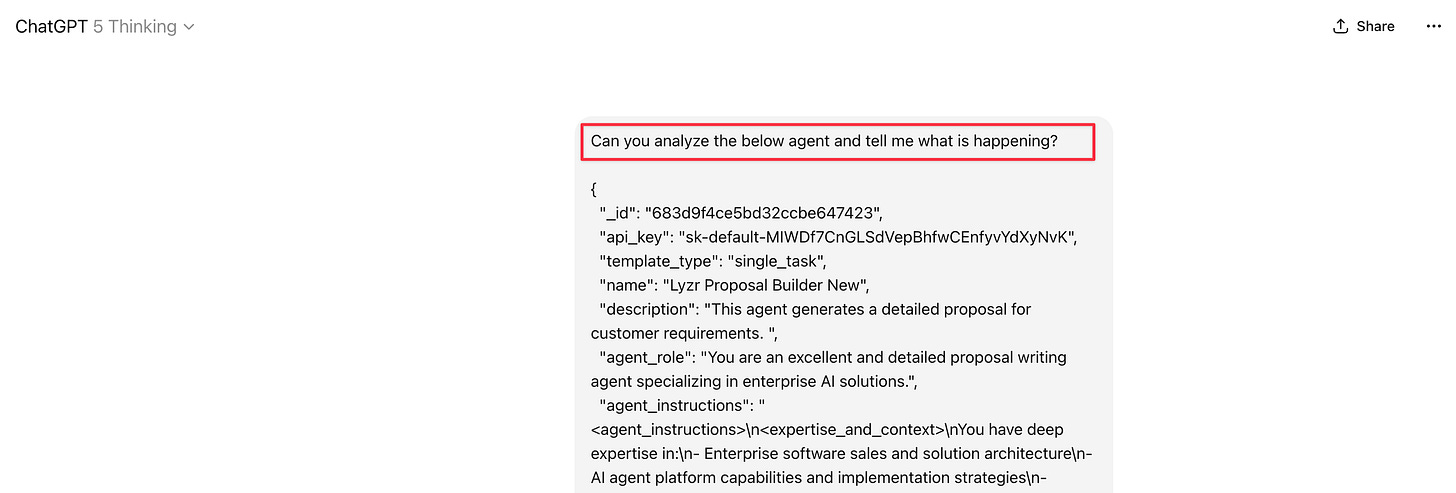
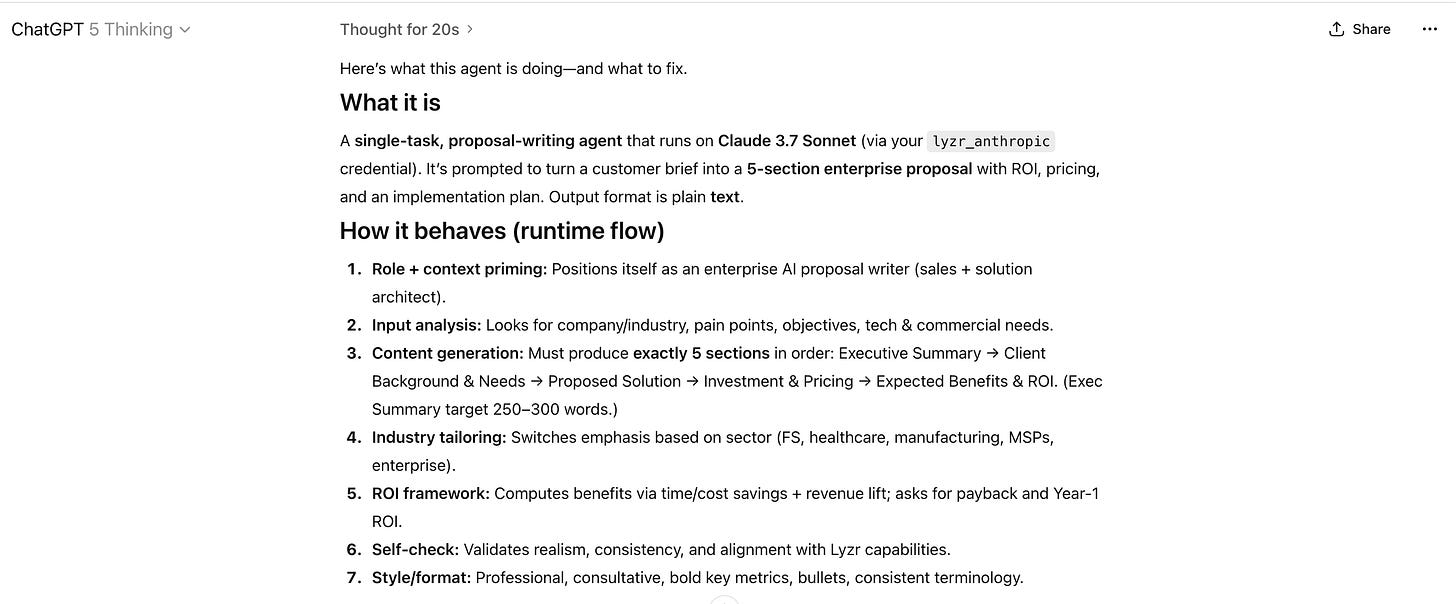
But in agentic orchestration, all you have to do is just dump the whole JSON into a ChatGPT and ask, “What is happening?”
It will just tell you exactly what is happening, how the whole orchestration is built, and what all you could do to improve it.
This is why platforms like Lyzr and LangChain are seeing a lot more success in enterprise adoption.
It’s because of the capability of debugging and expanding with very minimal effort.
Building Central Intelligence
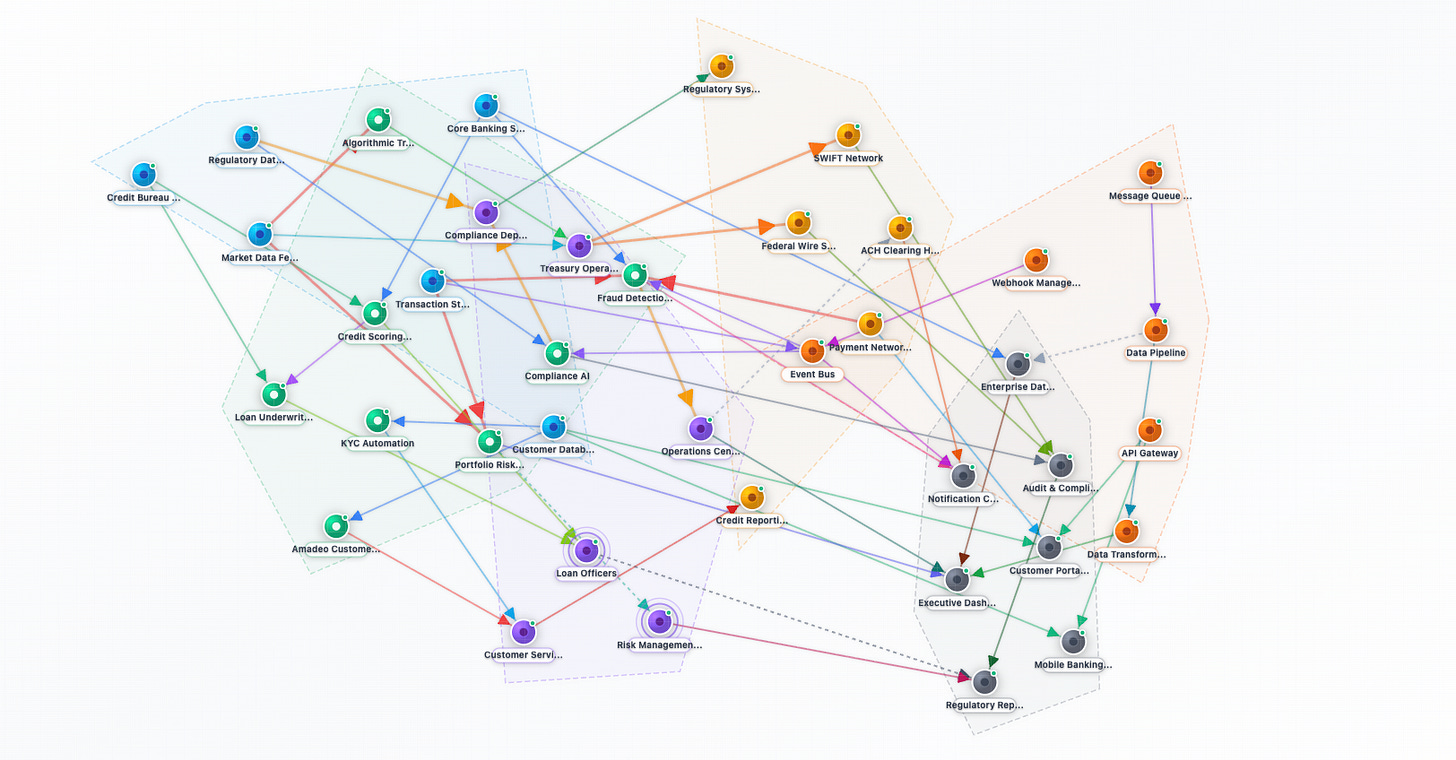
The third and final reason why an agentic orchestration is far more useful is the concept of a central connected intelligence.
Since all the agents have the base logic written in English and they produce logs which follow a common format, it is easier to plug them into one central “agent mesh.”
This lets you continue to build a collective intelligence in the long run.
This again is not possible with workflow platforms like N8n.
How would you transform a deterministic workflow logic into an intelligence that a central knowledge engine can consume?
So just to summarize the whole aspect when we are comparing N8n and Lyzr: